Introduction
Accessing the administration page of your website is achieved by appending ‘wp-admin’ to the end of the URL. If not logged in, a prompt for login credentials will appear.
The admin panel is the hub for content creation and management. A fundamental feature of a CMS is the separation of content and its presentation. While styling will be delved into later, this section primarily focuses on content creation and understanding the various content types within WordPress.
Content Types
WordPress categorises content into three default types:
- Posts: These are dynamic content pieces like blog articles, where authorship, publication date, and tags are relevant. This categorisation aids users in filtering and finding specific topics or author’s posts.
- Pages: These are static content pieces like home, about, or contact pages. Unlike posts, pages don’t have a publication date or author information as they are meant to be timeless and universal. Pages can have hierarchical relationships, for example, an FAQ page being accessible from the Contact page.
- Media: Media items such as images or videos are uploaded and hosted on the web server, with metadata like titles and alt text stored in the database. Media items can be reused across different pages and posts.
Custom Content Types
Custom content types cater to specific content needs. For instance, besides Posts and Pages, you might need Recipes, Product or Events. Utilising a plugin like Custom Post Type UI, enables the creation of custom content types.
Block Editor
With version 5.0, WordPress introduced the Gutenberg block editor, revolutionising content creation by allowing blocks of content to be added to pages or posts.
The block editor facilitates the addition of varied content blocks like Paragraph, Image, Gallery, Quote, List etc., providing a flexible editing environment.
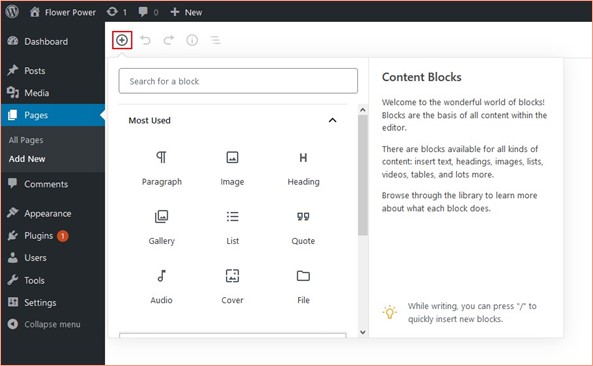
For a visual demonstration, refer to the WordPress essential training video linked below.
Plugins
Plugins extend the functionality of a standard WordPress installation. They are PHP software pieces that can be installed to add specific features, speeding up project development.
Plugins often come in free versions with basic functionality, and premium versions with additional features. With a vast ecosystem, it’s crucial to research and read reviews before installing plugins to ensure they meet your needs.
Key Plugins
Some widely used plugins include:
- WooCommerce: For creating an online store.
- Yoast SEO: For optimising your site for search engines.
- WordFence: For security, protecting against hackers and malware.
- Advanced Custom Fields: For adding custom fields.
- Custom Post Type UI: For creating custom content types.
Explore these plugins to understand their offerings and ascertain if they align with your project requirements.
WATCH
Video: WordPress 5 Essential Training 2. Content Management (11m)
Lesson Task
Brief
Install WooCommerce and use this plugin to create some sample products. Check these out on the front-end and experiment with different WooCommerce themes to see how the products are displayed differently.